Stream to 3D - Streaming
Streaming 2D Videos to 3D [NA for Real-Time Product]
This mode is accessed via the "Stream" menu button. Stream to 3D includes first class support for video streaming, which means that you can stream your real-time converted 2D to 3D videos to a host of devices including your phone, tablet, laptop, Smart TV or Projector (both 3D and 2D devices are supported) , as well as stream direct to your VR headset.
To stream a video and have it converted to 3D as it is streamed, click Stream in the main menu and select the file. If you have the Configuration Wizard enabled, then you will be prompted for your preferences on how you would like conversion and streaming to be handled, see here for detail on the Configuration Wizard prompts that will be presented. You can enable and disable the Configuration Wizard or put it in "auto" mode from Settings. When disabled, or in "auto" mode, the Wizard preference questions are not displayed.
The video below provides a comprensive set of streaming examples to a range of devices and media players using the various supported protocols. Note that streaming with subtitles is only supported over the Http Streaming protocol:
HTTP streaming is the default. However, Stream to 3D also supports; RTP, UDP and RTSP streaming. These can be selected and configured in the "Settings/Streaming" menu:
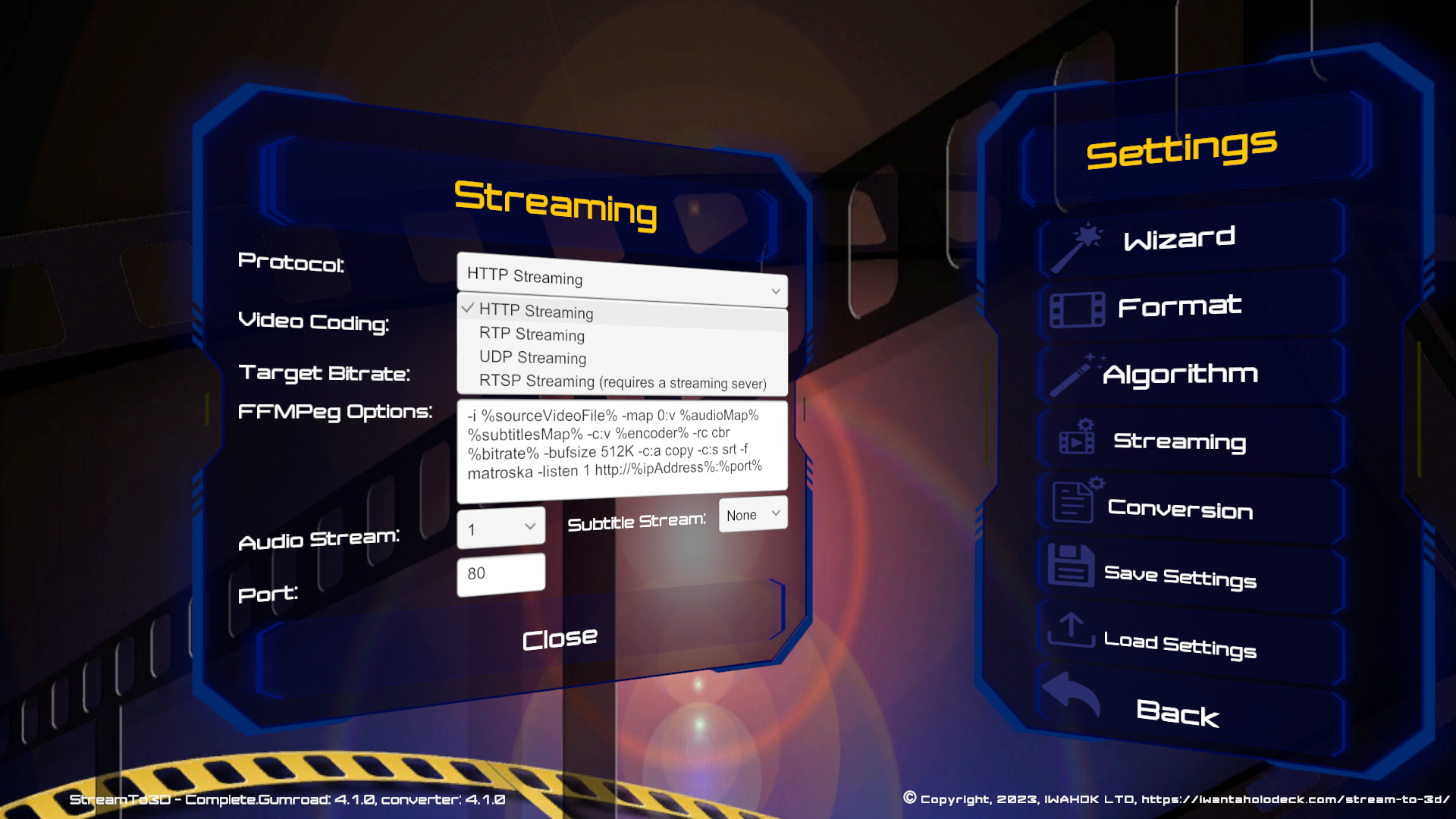
The Pros and Cons of the different protocols are discussed here. HTTP is the most widely supported.
Note that the use of the RTSP protocol with Stream to 3D also requires a streaming server such as Media MTX. Media MTX is actually very easy to setup, just download the release zip for Windows and run the "mediamtx.exe" application while Stream to 3D is running. RTSP streaming with Stream to 3D will then operate with the Media MTX defaults, without further configuration.
Audio Stream selection, using the numerical index of the required audio stream, is available for all protocols. Subtitle Streaming is only available for Http video streaming, again by selection of the required stream by its numerical index.
You can control the Video coding, GPU acceleration and detail of the FFMPeg Options used for streaming as described here. The settings page also let's you specifiy the port that should be used for each protocol. The ip address portion of the streaming URL is determined by Stream to 3D automatically, as the IP address of the machine on which Stream to 3D is running.
Stream to 3D will display the streaming URL, that will be used by the currently selected streaming protocol (as selected in "Settings/Streaming"), in the Output section of the Settings Summary Page. You should open this URL with your client media player to access the video stream:
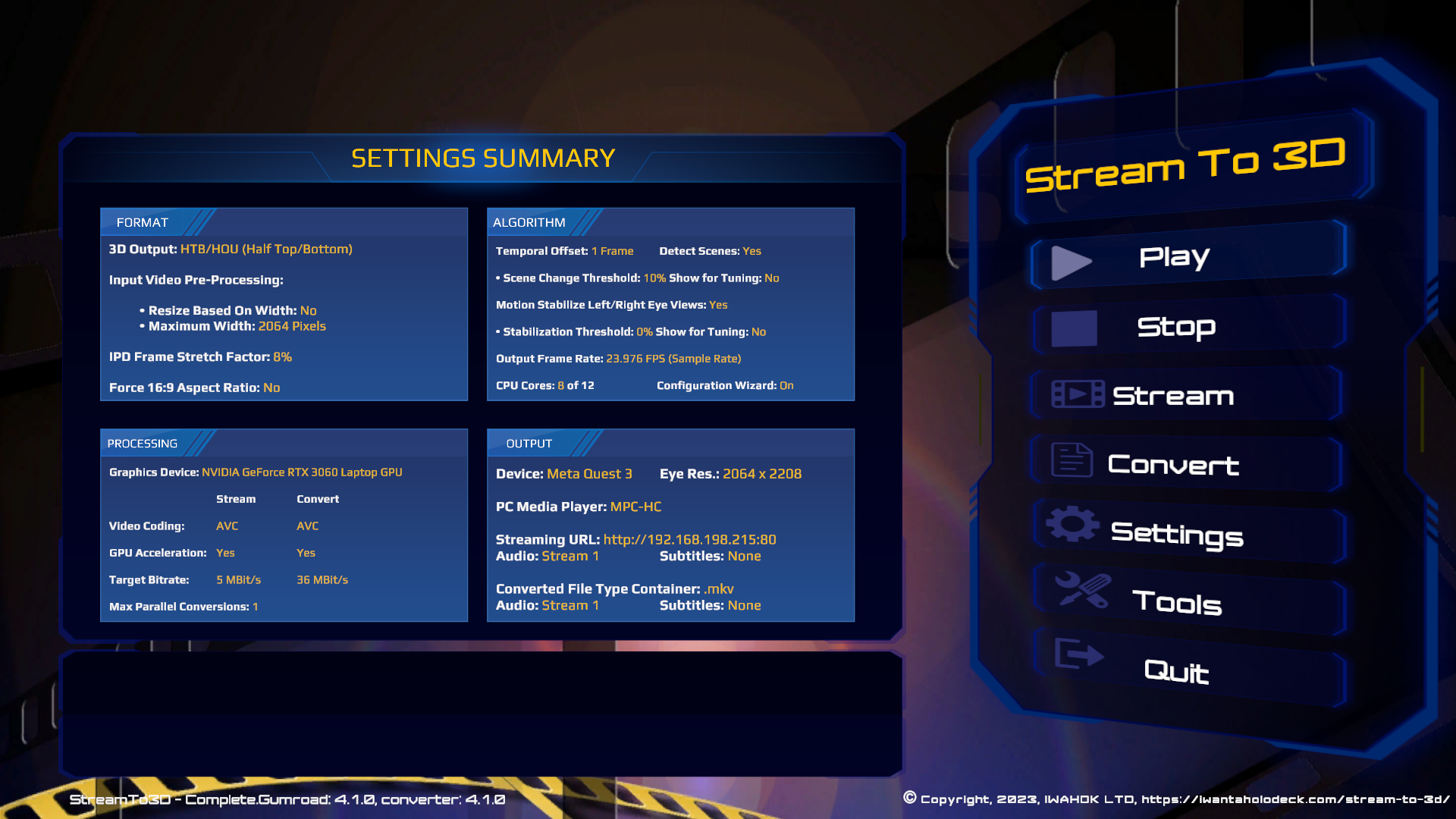
Example media players that support streaming include; VLC for Desktop and PotPlayer on the PC, the Pigasus VR Media player (on an Oculus Quest 2 or later headset) and VLC for Fire (for a Fire TV Stick) as well as Kodi. Examples for these media players are provided below, for more comprehensive coverage, see the video above.
To initiate streaming, click the Stream button. You will be prompted to select either a 2D video to convert to 3D and stream, or if the video is already in 3D format, as determined by the same file name pattern check as used for playback and conversion, then the video will be streamed only. For the broadcast streaming protocols, which does not include Htpp, it is also possible to provide a .txt file containing the path names of videos to stream, these will then be streamed one after the other, like a play list:
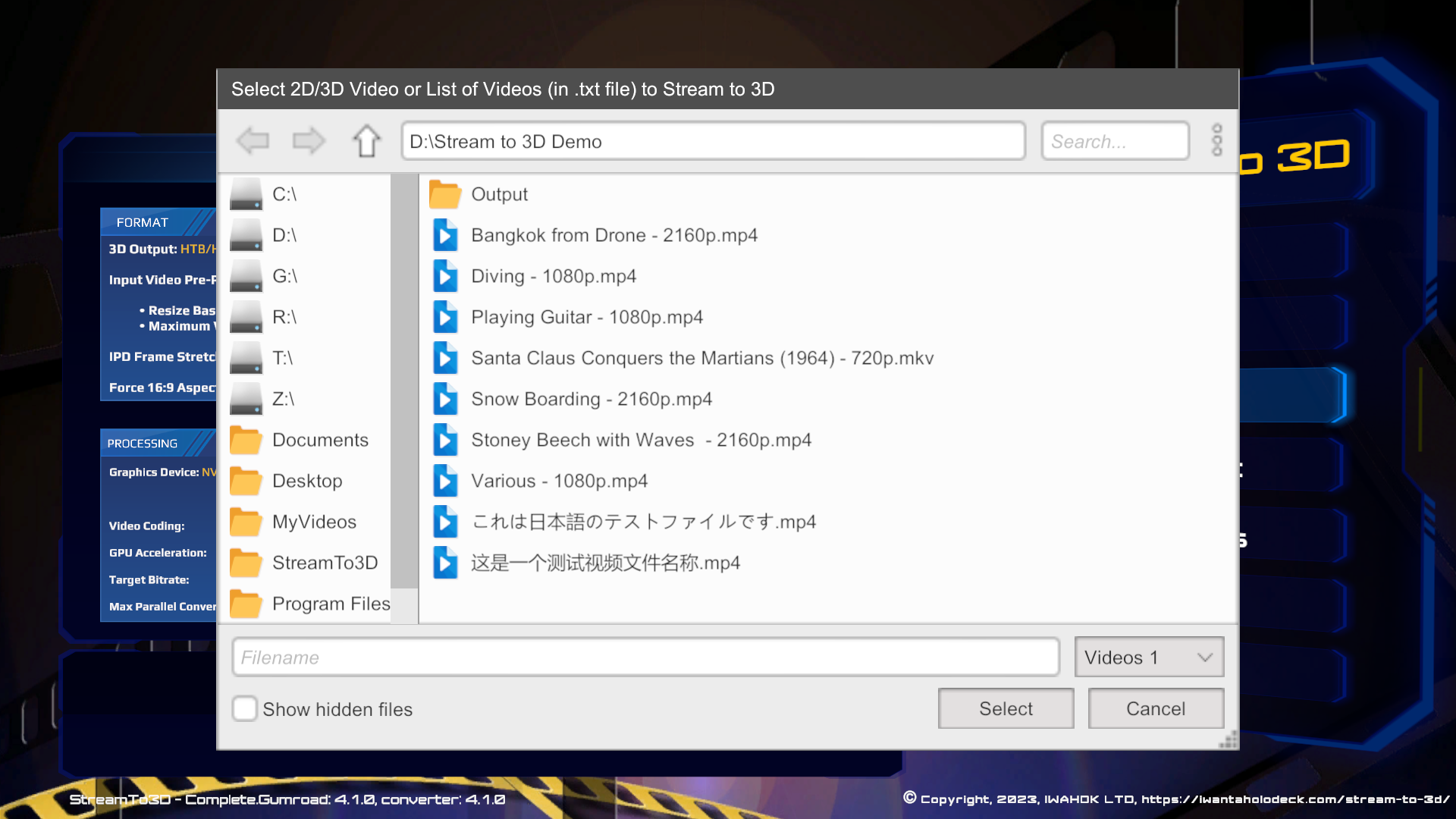
For HTTP Streaming, Stream to 3D will wait until the client opens the stream before streaming the video, for the other protocols Stream to 3D will start streaming the video(s) immediately and the media player will pick up the video stream from the point it has reached when opened by the player, rather than the start:
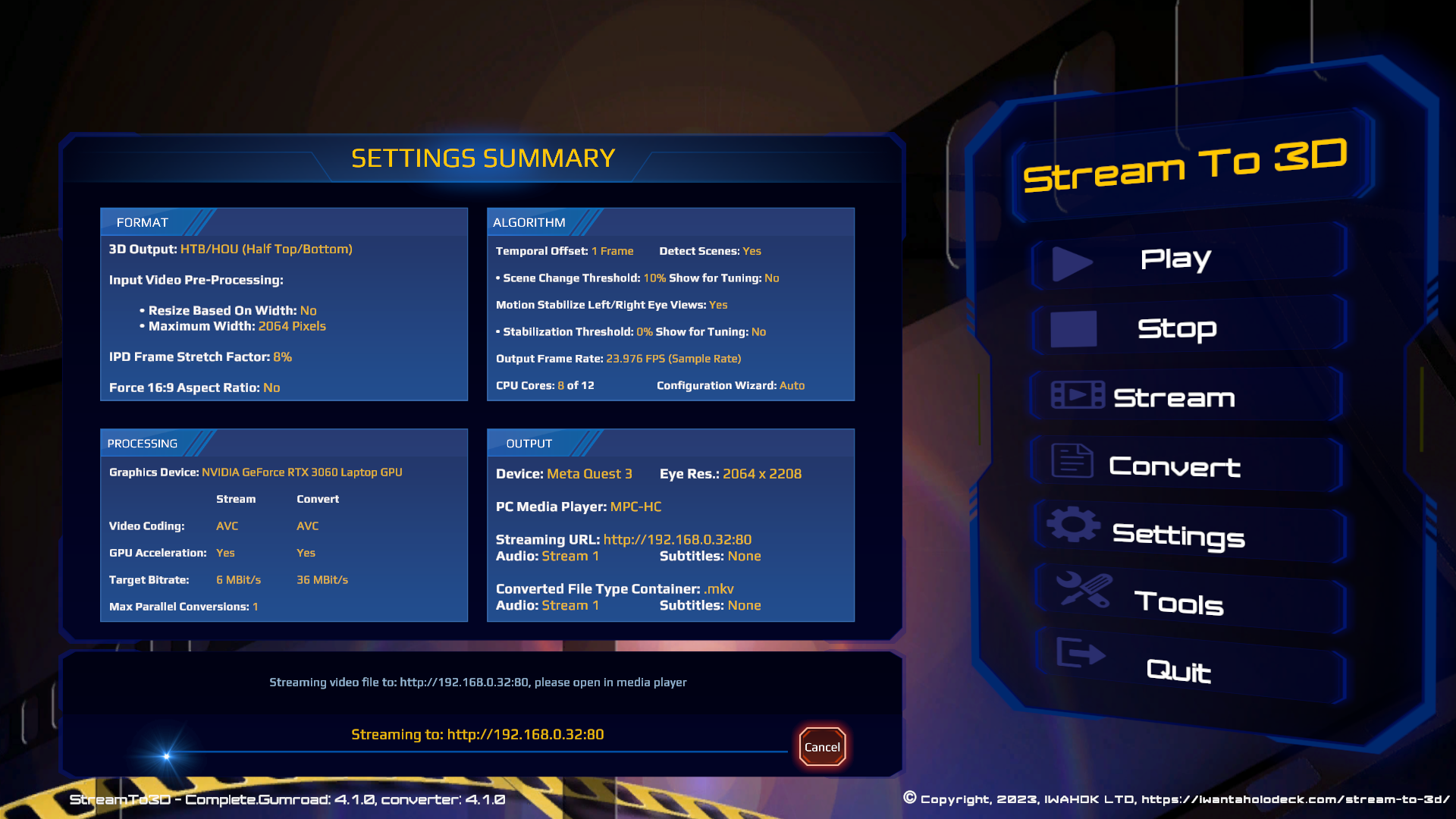
As the video is streamed, you will be shown a progress bar detailing the time taken to convert and stream the video, with an estimate of the time remaining to complete, the percentage progress and the name of the file being streamed. The streaming process attempts to stream the video at the frame rate of the converted source, not faster. If your system cannot handle converting and streaming the video at the required frame rate, then playback may be interrupted or intermittent. The Cancel button presented will allow you to cancel a video that is in the process of being streamed:
VLC for Desktop
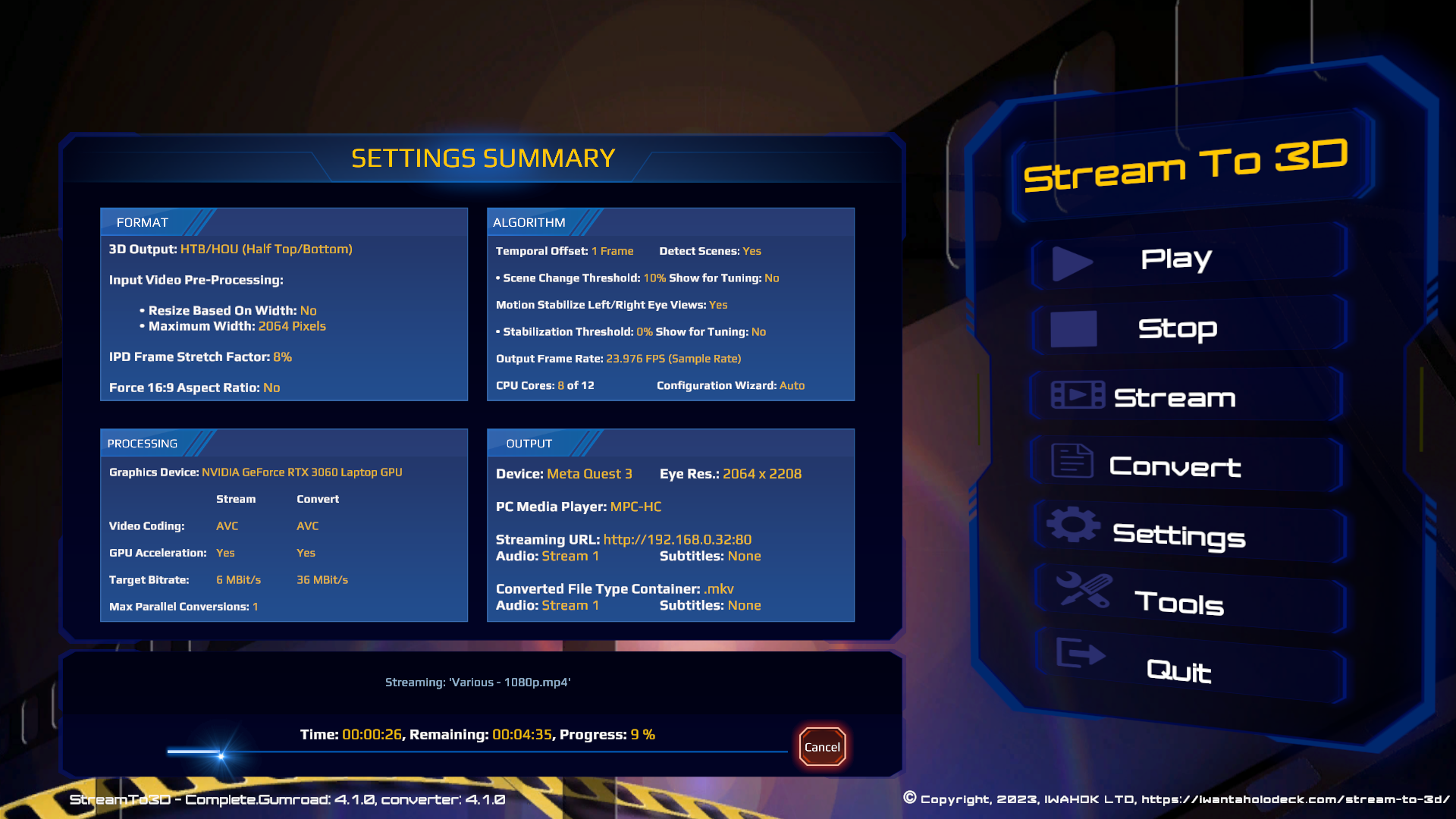
The video stream is Opened in VLC for Desktop via the "Media/Open Network Stream..." menu option as illustrated below:

This will then lead to the "Open Media" dialog box, in which you should enter the streaming URL shown by Stream to 3D. Pressing play will cause VLC to initiate playback of the video stream. VLC will remember the URL for later sessions, which will then be available in the network url drop down list. VLC for Desktop also supports the RTP and RTSP streaming protocols in addition to HTTP:
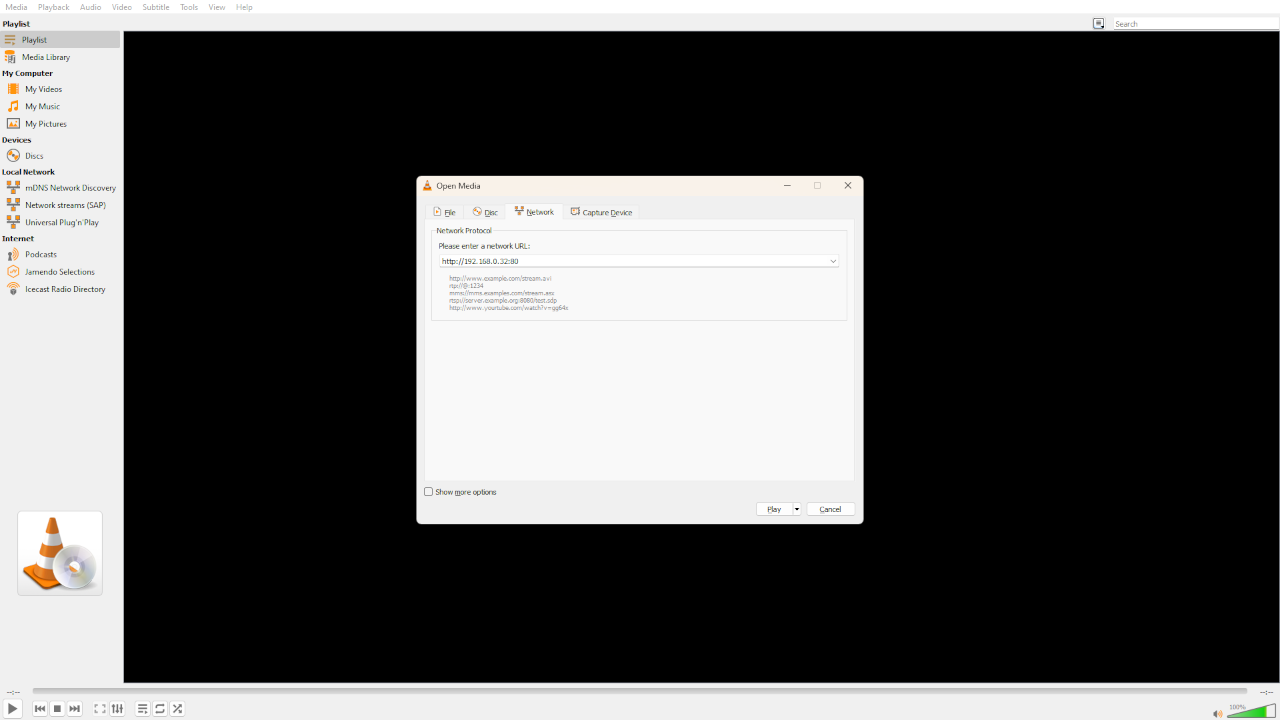
The screen shot below shows the streamed video being played in VLC:
Pigasus VR Media Player
The video below provides an example of HTTP Streaming with the Pigasus VR Media player, running on an Oculus Quest 2 headset. N.B. for use with Pigasus it is most effective to open the HTTP Streaming URL in Pigasus before selecting the video in the Stream to 3D UI. Pigasus also supports RTSP:
Kodi Media Player
Kodi essentially requires the creation of a ".strm" file containing the Stream to 3D streaming URL. Opening the ".strm" file with Kodi will then cause Kodi to initiate streaming from Stream to 3D, provided Stream to 3D is up and running and ready to stream. For more details, see Kodi setup for Stream to 3D here. The use of Kodi for playback, via streaming or indeed from a converted file, on a 3D Projector or TV (via installation on a Fire TV Stick for example), is a very effective solution for 3D Playback.
VLC for Fire (with 3D TV)
The example below uses the VLC for Fire app, on a 4K Fire TV stick plugged into a 4K LG passive 3D TV. Begin with the Streams option in the VLC for Fire app. The VLC for Fire app supports both HTTP and RTSP streaming:
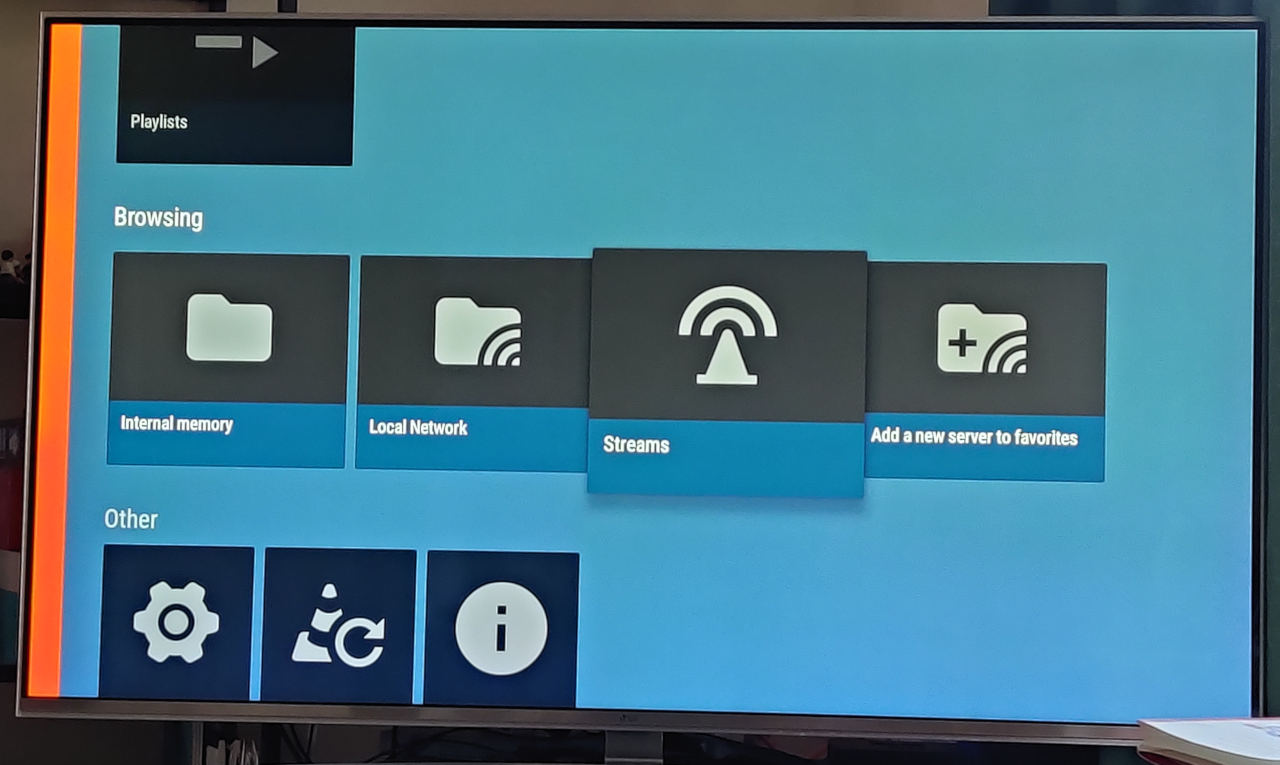
On the next screen either enter the HTTP (or RTSP) streaming URL or select from a previously used URL:
The video will then play back in a 3D format on the TV (in this example). If you have a 2D rather than a 3D TV, you can experiment with the Anaglyph 3D output format, as this is viewable with Red/Cyan glasses on a 2D device:

This particular LG TV supports 3D HSBS and HTB formats, the next screen shows selection of the HSBS format:

The video then plays back in 3D and is viewable with passive 3D polarised glasses on this particular TV:

Click here to go to the Usage and Configuration home page.